To understand dubbing and voice-over, the important thing to know is that, technically, voice-over is a kind of dubbing. When some information needs to be passed through audiovisual media in multiple languages, it can be done in two ways. One method is by using subtitles, and the other is by re-voicing the initial soundtrack. Voice-over and dubbing are re-voicing techniques intended at converting an already existing product for a different market.
When it comes to translating audiovisual content into different languages, two popular methods are commonly used: voice-over and dubbing. Both approaches serve the purpose of audio localization, enabling viewers to understand and engage with content in their native languages. This article explores the differences between voice-over and dubbing and provides insights into choosing the right approach for effective audio localization.
Voice-over:
Voice-over involves overlaying the original audio with a translated voice track, while the original audio remains audible in the background. Here are some key considerations for voice-over:
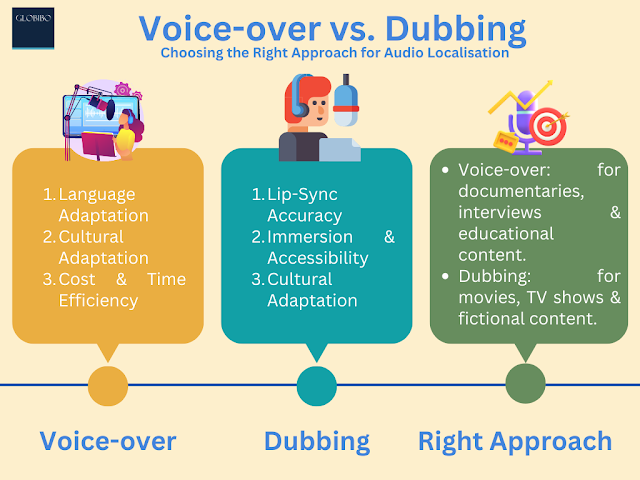
1.1 Language Adaptation: Voice-over allows the original dialogue to be preserved, maintaining the authenticity and tone of the original performance. The translated voice track is synchronized with the original audio, ensuring that the viewer can still hear the original actors’ voices.
1.2 Cultural Adaptation: Voice-over offers flexibility in adapting cultural nuances and expressions. Translators can modify the dialogue to ensure it resonates with the target audience, while still conveying the original message. This approach allows for a certain degree of localization while retaining the original visuals and performances.
1.3 Cost and Time Efficiency: Voice-over is generally less expensive and faster to produce compared to dubbing. Since only the translated voice track needs to be recorded and synchronized, it requires fewer resources and can be completed relatively quickly.
Dubbing:
Dubbing involves replacing the original audio with a translated version, synchronized with the actors’ lip movements. Here are some key considerations for dubbing:
2.1 Lip-Sync Accuracy: Dubbing aims to create an illusion of natural lip movements matching the translated dialogue. The translated audio is carefully synchronized with the actors’ lip movements, ensuring a seamless viewing experience for the audience.
2.2 Immersion and Accessibility: Dubbing allows viewers to fully immerse themselves in the content without the distraction of the original language. It eliminates the need for reading subtitles, making the content more accessible to a wider audience, including those who may have difficulty reading or following subtitles.
2.3 Cultural Adaptation: Dubbing offers the opportunity to adapt not only the dialogue but also the vocal performances to align with the cultural norms and preferences of the target audience. This level of localization helps create a more authentic and relatable experience for viewers.
2.4 Quality and Production Considerations: Achieving high-quality dubbing requires skilled voice actors who can accurately portray the original actors’ emotions and deliver a natural performance. Additionally, the dubbing process involves careful audio mixing and post-production work to ensure optimal sound quality.
Choosing the Right Approach:
The choice between voice-over and dubbing depends on various factors, including the nature of the content, target audience preferences, budget, and time constraints. In general:
Voice-over is suitable for documentaries, interviews, educational content, and cases where preserving the original audio is important. It is cost-effective and allows for more flexibility in language and cultural adaptation.
Dubbing is commonly used for movies, TV shows, and fictional content, where lip-sync accuracy and immersive viewing experience are crucial. It provides seamless audiovisual integration and enhances accessibility for a broader audience.
Deciding between voice-over and dubbing is a crucial step in audio localization for audiovisual content. Both approaches have their strengths and considerations. Understanding the differences and weighing factors such as language adaptation, cultural adaptation, cost, and audience preferences will help you make an informed decision and ensure effective communication and engagement with the target audience.
Off-screen voice-overs are aimed at replacing original dialogues in products like radio commercials or video games. Whereas in other kinds of voice-overs, the original dialogue is not replaced.
Dubbing is aimed at fully replacing the original dialogue. The audio in dubbing is synced with the movement of the lips of the on-screen actors. This makes it even more precise and authentic when compared to voice-overs.
Voice-overs have different styles, like UN-style, off-camera or narration, and lecturing. In UN-style voice-overs, the original sound or dialogue can be heard faintly in the background, along with the translated voice-over playing prominently in the foreground. This method is frequently used for news reports, interviews, and speeches. Narrations are either added to pre-existing content or are played by themselves. They are usually used in radio commercials, documentaries, and podcasts. Lektoring, a style popular in Poland, is a process where a single person, usually a male, reads the translated content.